Overview – Liver Cancer
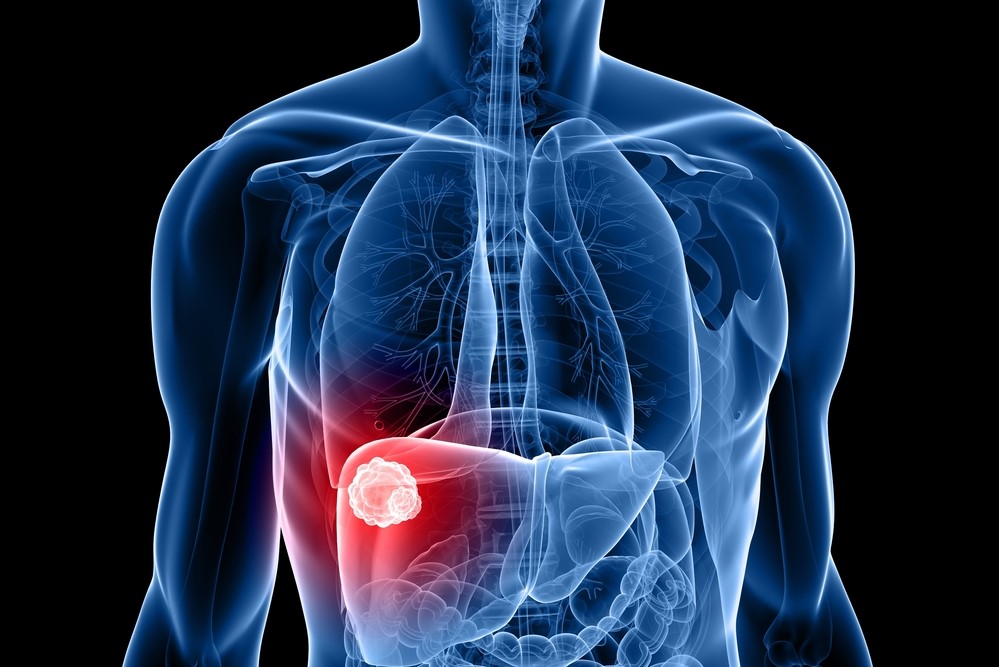
Hepatocytes are the main functioning cells of the liver. Certain factors cause these cells to grow and multiply uncontrollably leading to the formation of tumors. These tumors are known as hepatoma and they destroy and invade normal healthy cells. This is primary liver cancer and it is also known as hepatocellular carcinoma. Primary liver cancer is also caused by the growth and spread of cancerous cells in the tubes that transport bile. In some cases, liver cancer may occur as a result of cancer that has originated in another part of the body. This usually happens when cancer cells from the lungs, breast, colon, stomach, or the pancreas break off and spread to the liver. This type of liver cancer is known as secondary or metastatic cancer.
Causes of liver cancer
People who suffer from chronic liver diseases such as cirrhosis are susceptible to liver cancer. Hepatitis virus infection, excessive alcohol consumption, and smoking are some of the major causes of cirrhosis. Obesity and hemochromatosis (which causes iron levels in the blood to increase) can also cause cirrhosis. Prolonged exposure to certain substances such as herbicides, arsenic, and vinyl chloride can increase the risk of liver cancer.
Diseases such as Wilson’s disease and diabetes can make a person susceptible to liver cancer. Nonalcoholic fatty liver disease, which leads to the accumulation of fat in the liver, increases the probability of liver cancer.
Symptoms of liver cancer
There are no apparent symptoms in the early stages of liver cancer. As the size of the tumor starts growing, a person may start to experience pain in the abdomen, specifically on the right side. A person may feel full despite eating only a little amount of food. Once the cancer is in the advanced stage, a person may experience the following symptoms-
- Sudden unexplained loss of weight
- Itching
- Fever and jaundice
- Vomiting and nausea
- Fatigue and general weakness
- Back pain
- Enlarged liver
- Appetite loss
- White, chalky stools
Diagnosis of liver cancer
If the above symptoms are observed, a doctor might suggest the following tests to diagnose liver cancer-
- Imaging tests
Imaging tests such as CT scan, ultrasound, and MRI may help to detect the growth of tumors in the liver. - Blood tests
Liver function anomalies are often detected through various blood tests. - Liver biopsy
This procedure involves the removal of a small piece of liver tissue. A thin needle is inserted into the liver through the skin and a small tissue sample is extracted. The sample is then studied and tested under a microscope for the presence of cancer cells.
Treatment of liver cancer
Liver cancer treatment depends on the stage of cancer. The type of treatment also depends on the patient’s overall health and age. In the early stages, surgery can be used to remove the cancerous cells. In the early stages, localized treatments such as heating cancer cells, freezing the cells, injecting chemotherapy medications directly to the cancer cells. Other treatments for liver cancer include radiation therapy, targeted therapy, and liver transplant surgery.