Treating and Managing High Cholesterol
Consistently having high levels of cholesterol can magnify the risk of cardiovascular diseases and strokes. Therefore, to evade such complications, it is important to keep high cholesterol in check. In most cases, high cholesterol is the result of unhealthy diet and sedentary lifestyle. However, with the right treatments and self-management measures, one can successfully control the cholesterol and maintain a healthy heart functions.
Medical treatments for high cholesterol
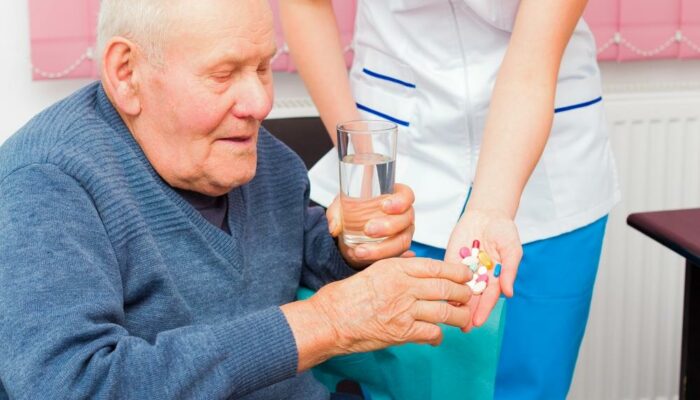
A medication course for bad cholesterol will be implemented if it can’t be merely controlled by lifestyle changes and diet. The type and amount of medications recommended will depend on multiple factors like age, current health conditions, and individuals risk factors. Moreover, the doctor might even have to make modifications in the medications or dosage patterns if they cause side-effects or prove to be ineffective. Here are some of the common prescription medications used to treat high cholesterol.
- Statins – Statins obstruct substances in your liver that are instrumental in producing cholesterol, thereby leading to the elimination of low-density lipoprotein (LDL), which is the bad cholesterol from the blood. Furthermore, these drugs even reabsorb accumulated cholesterol from the artery walls, which facilitates the free flow of blood.
- Absorption inhibitors – The small intestine retains the cholesterol from your food and directs it into the blood. The absorption inhibitors lower the blood cholesterol levels by restricting the absorption of dietary cholesterol.
- Bile acid binding resins – The liver uses cholesterol to produce digestive enzymes known as bile acids. The bile acid binding resins induce the liver to use the extra cholesterol to yield more bile acid which lower its concentrations in your blood.
- Injectable medications – A new class of drugs, injectable medications allow the liver to absorb a greater amount of bad cholesterol. These are generally used for individuals who have had a medical history of heart disease and project intolerance to other types of cholesterol controlling medications.
If your triglycerides (a type of fat) levels are high as well, then your medical practitioner will prescribe additional medications such as fibrates and omega-3 fatty acid supplements. However, before using over-the-counter (OTC) omega-3 fatty acid supplements, ensure to discuss it with your doctor to avoid any side effects.
Tips for controlling high cholesterol
The essential part of cholesterol management is a disciplined lifestyle and nutritious diet. Hence, devise a suitable plan with your medical practitioner to control bad cholesterol.
- Healthy diet – Your diet directly influences your blood cholesterol levels, therefore, make a conscious effort to eat foods that are beneficial to your heart. These include fresh fruits and vegetables, whole grains, fatty fish like salmon, herring or mackerel, low-fat dairy, and foods having healthy fats like almonds, avocados, walnuts or pecans. Conversely, avoid full-fat dairy products, organ meats, foods comprising saturated or trans-fat or refined sugars. Likewise, ensure that you drink alcohol in moderation or cut it out completely.
- Workout regularly – Exercising every day encourages the blood flow as well as burns excess cholesterol. A regular workout regime is important if you’re overweight. Losing a few pounds can lower the strain on your body and boost your heart functions. Consult your doctor about the most effective and safe options to lose weight. You can try brisk walks, swimming, cycling, running or yoga to bring your weight under control. Exercise every day for at least 30 minutes.
- Quit smoking – Smoking increases inflammation in the body and damages the blood vessels and arteries as it accelerates the buildup of plaque. Consequently, this can lead to the onset of heart disorders. Although quitting smoking is easier said than done, it isn’t impossible. A complete abstinence from smoking can be achieved with the help of counseling, nicotine patches, and electronic cigarettes.